반응형
- 참고 : 이수안컴퓨터연구소
모델 정의
nn.Module 상속 클래스 정의
- nn.Module을 상속받는 클래스 정의
- init(): 모델에서 사용될 모듈과 활성화 함수 등을 정의
- forward(): 모델에서 실행되어야 하는 연산을 정의
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inputs):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.layer = nn.Linear(inputs, 1)
self.activation = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layer(x)
x = self.activation(x)
return x
model = Model(1)
print(list(model.children()))
print(list(model.modules()))
>> [Linear(in_features=1, out_features=1, bias=True), Sigmoid()]
[Model(
(layer): Linear(in_features=1, out_features=1, bias=True)
(activation): Sigmoid()
), Linear(in_features=1, out_features=1, bias=True), Sigmoid()]
nn.Sequential을 이용한 신경망 정의
- nn.Sequential 객체로 그 안에 각 모듈을 순차적으로 실행
- init()에서 사용할 네트워크 모델들을 nn.Sequential로 정의 가능
- forward() 에서 실행되어야 할 계산을 가독성 높게 작성 가능
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels = 3, out_channels = 64, kernel_size = 5),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(2)
)
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels = 64, out_channels = 30, kernel_size = 5),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(2)
)
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features = 30*5*5, out_features = 10, bias = True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
x = self.layer3(x)
return x
model = Model()
모델 파라미터
손실 함수(Loss function)
- 예측 값과 실제 값 사이의 오차 측정
- 학습이 진행되면서 해당 과정이 얼마나 잘 되고 있는지 나타내는 지표
- 모델이 훈련되는 동안 최소화될 값으로 주어진 문제에 대한 성공 지표
- 손실 함수에 따른 결과를 통해 학습 파라미터를 조정
- 최적화 이론에서 최소화 하고자 하는 함수
- 미분 가능한 함수 사용
- 파이토치의 주요 손실 함수
- torch.nn.BCELoss : 이진 분류를 위해 사용
- torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss : 다중 클래스 분류를 위해 사용
- torch.nn.MSELoss : 회귀 모델에서 사용
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
옵티마이저(Optimizer)
- 손실 함수를 기반으로 모델이 어떻게 업데이트되어야 하는지 결정 (특정 종류의 확률적 경사 하강법 구현)
- optimizer는 step()을 통해 전달받은 파라미터를 모델 업데이트
- 모든 옵티마이저의 기본으로 torch.optim.Optimizer(params, defaults) 클래스 사용
- zero_grad()를 이용해 옵티마이저에 사용된 파라미터들의 기울기를 0으로 설정
- torch.optim.lr_scheduler를 이용해 에포크(epochs)에 따라 학습률(learning rate) 조절
- 파이토치의 주요 옵티마이저: optim.Adadelta, optim.Adagrad, optim.Adam, optim.RMSprop, optim.SGD
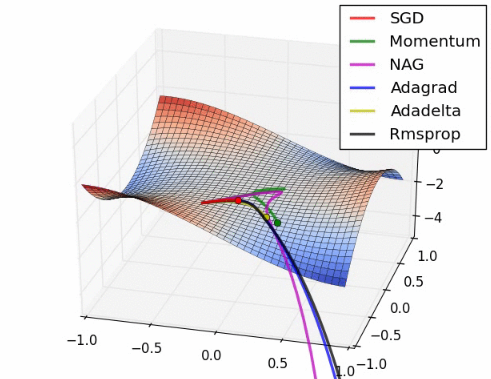
지표(Metrics)
- 모델의 학습과 테스트 단계를 모니터링
import torchmetrics
metric = torchmetrics.Accuracy(task="multiclass", num_classes=5)
n_batches = 10
for i in range(n_batches):
preds = torch.randn(10, 5).softmax(dim= -1)
target = torch.randint(5, (10,))
acc = metric(preds, target)
print(acc)
acc = metric.compute()
print(acc)
선형 회귀 모델(Linear Regression Model)
- 데이터 생성
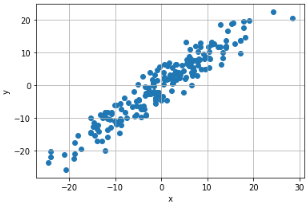
X = torch.randn(200, 1) * 10 y = X + 3 * torch.randn(200, 1) plt.scatter(X.numpy(), y.numpy()) plt.ylabel('y') plt.xlabel('x') plt.grid() plt.show()- 모델 정의 및 파라미터
class LinearRegressionModel(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(LinearRegressionModel, self).__init__() self.linear = nn.Linear(1,1) def forward(self, x): pred = self.linear(x) return pred model = LinearRegressionModel()- 기본으로 적용된 가중치값으로 회귀선 확인
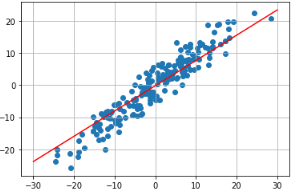
w, b = model.parameters() w1, b1 = w[0][0].item(), b[0].item() x1 = np.array([-30,30]) y1 = w1 * x1 + b1 plt.plot(x1,y1,'r') plt.scatter(X,y) plt.grid() plt.show()- 손실 함수 및 옵티마이저
import torch.optim as optim criterion = nn.MSELoss() optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)- 모델 학습

- 회귀선 적용
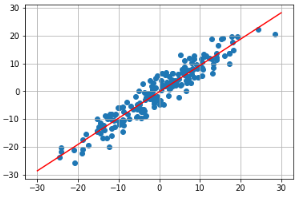
w1, b1 = w[0][0].item(), b[0].item() x1 = np.array([-30,30]) y1 = w1 * x1 + b1 plt.plot(x1,y1,'r') plt.scatter(X,y) plt.grid() plt.show()
- 회귀선 적용
epochs = 100 losses = [] for epoch in range(epochs): optimizer.zero_grad() y_pred = model(X) loss = criterion(y_pred, y) losses.append(loss.item()) loss.backward() optimizer.step()
FashionMNIST 분류 모델
- gpu 설정
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu') device >> device(type='cuda')
데이터 로드
transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, ), (0.5, ))]
)
trainset = datasets.FashionMNIST(root='/content/',
train=True, download=True,
transform=transform)
testset = datasets.FashionMNIST(root='/content/',
train=False, download=True,
transform=transform)
train_loader = DataLoader(trainset, batch_size = 128, shuffle=True, num_workers=2)
test_loader = DataLoader(trainset, batch_size = 128, shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
images, labels = next(iter(train_loader))
images.shape, labels.shape- 로드된 데이터 확인
labels_map = {
0 : 'T-Shirt',
1 : 'Trouser',
2 : 'Pullover',
3 : 'Dress',
4 : 'Coat',
5 : 'Sandal',
6 : 'Shirt',
7 : 'Sneaker',
8 : 'Bag',
9 : 'Ankle Boot'
}
figure = plt.figure(figsize = (12,12))
cols, rows = 4, 4
for i in range(1, cols * rows + 1):
image = images[i].squeeze()
label_idx = labels[i].item()
label = labels_map[label_idx]
figure.add_subplot(rows,cols,i)
plt.title(label)
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(image, cmap='gray')
plt.show()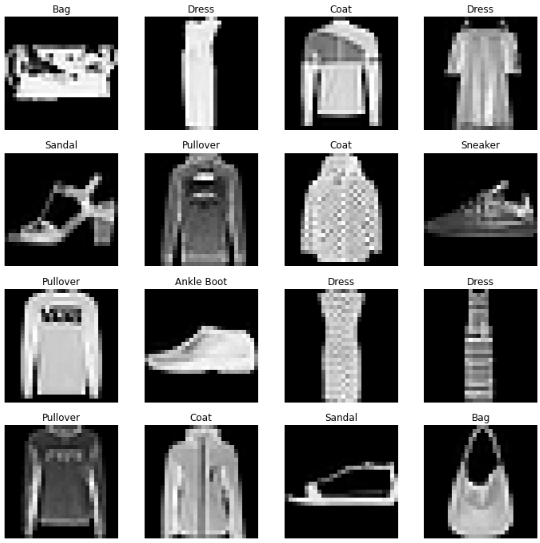
모델 정의 및 파라미터
import torch.nn.functional as F
class NeuralNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(NeuralNet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 3)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 3)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5* 5 ,120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120 ,84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84 ,10)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2,2))
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2)
x = x.view(-1, self.num_flat_features(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
def num_flat_features(self, x):
size = x.size()[1:]
num_features = 1
for s in size:
num_features *= s
return num_features
net = NeuralNet()
손실함수와 옵티마이저
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr = 0.001, momentum=0.9)
모델 학습
- 배치수 확인
total_batch = len(train_loader)
print(total_batch)
>> 469
for epoch in range(10):
running_loss = 0.0
for i, data in enumerate(train_loader, 0):
inputs, labels = data
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
if i % 100 == 99:
print(f'Epoch: {epoch + 1}, iter : {i+1}, Loss : {running_loss/2000}')
running_loss = 0.0
모델의 저장 및 로드
- torch.save : net.state_dict()를 저장
- torch.load : load_state_dict로 모델을 로드
PATH = './fashion_mnist.pth'
torch.save(net.state_dict(), PATH)
net = NeuralNet()
net.load_state_dict(torch.load(PATH))
모델 테스트
def imshow(image):
image = image / 2 + 0.5
npimg = image.numpy()
fig = plt.figure(figsize = (16,8))
plt.imshow(np.transpose(npimg, (1,2,0)))
plt.show()
import torchvision
dataiter = iter(test_loader)
images, labels = dataiter.next()
imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(images[:6]))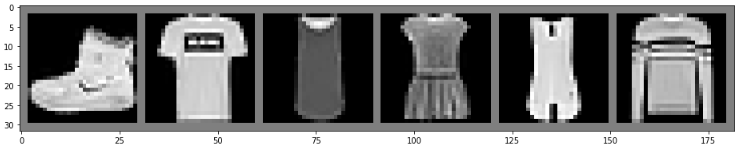
output = net(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(output, 1)
print(predicted)
>> tensor([9, 0, 6, 6, 3, 2, 7, 4, 5, 5, 0, 9, 5, 5, 7, 9, 1, 0, 6, 4, 3, 1, 4, 8,
4, 3, 0, 2, 4, 4, 5, 3, 6, 6, 0, 8, 5, 2, 1, 6, 6, 7, 9, 5, 5, 2, 7, 3,
0, 3, 3, 3, 7, 2, 2, 0, 6, 8, 3, 3, 5, 6, 5, 5, 6, 2, 0, 0, 4, 1, 3, 1,
0, 3, 1, 4, 4, 0, 1, 9, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 7, 1, 7, 9, 9, 9, 3, 6, 9, 3, 6,
6, 1, 1, 8, 8, 3, 1, 1, 6, 8, 1, 9, 7, 8, 8, 9, 6, 6, 3, 1, 5, 4, 6, 7,
5, 5, 9, 2, 2, 2, 7, 1])
print(''.join('{}, '.format(labels_map[int(predicted[j].numpy())]) for j in range(6)))
>> Ankle Boot, T-Shirt, Shirt, Shirt, Dress, Pullover
correct = 0
total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data in test_loader:
images, labels = data
outputs = net(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
print(100 * correct / total)
>> 83.27833333333334반응형
'Study > Self Education' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Pytorch 기본기 - 5 (0) | 2024.07.02 |
|---|---|
| Pytorch 기본기 - 4 (0) | 2024.07.02 |
| Pytorch 기본기 - 2 (0) | 2024.07.02 |
| Pytorch 기본기 - 1 (0) | 2024.07.02 |
| 핸즈온 머신러닝 - 14 (0) | 2024.06.19 |
